Feeding hungry people with donations of extra food is an integral part of resource conservation. Organizations served by food rescue and food bank programs include community centers, soup kitchens, food pantries, homeless shelters, senior programs, and childcare centers.
- Food rescue means recovering healthy foods and making fast deliveries to those in need. This is the highest and best use for perishable food. The Fresno Metro Ministry Food Recovery project, which takes excess perishable food to hungry people, is an example.
- Food Finders is a community-based food rescue organization in Southern California, which serves as a conduit, between donors and people in need.
- Food rescue in Southern California also includes Waste Not OC Coalition which works to help meet the nutritional needs of the community by facilitating the donation and distribution of surplus food.
- Food banks are organizations that collect food from a variety of sources, and distribute it to hungry people through local service agencies. The California Association of Food Banks which has a membership of 43 food banks, is one of the leading organizations in California. Major programs include Farm to Family which works with growers and packers to provide fresh produce to banks.
Food Donation
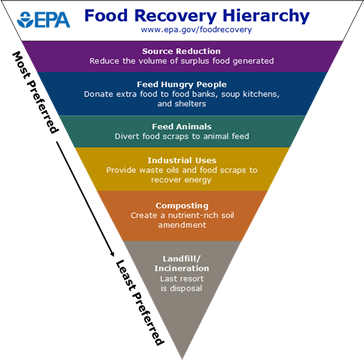
The US EPA’s Food Recovery Hierarchy ranks food donations to feed hungry people as a top priority to help reduce wasted food. The top levels of the hierarchy are the best ways to prevent waste and bring most benefits for the environment.
Food Donations in your community
- Food donors include food processors and manufacturers, grocers, wholesalers, farmers, and organized community food drives.
- Perishable and prepared foods are typically collected from restaurants, caterers, corporate dining rooms, and hotels for prompt distribution to hungry people in their communities.
- Donated food includes edible food from events, products affected by labeling regulations or manufacturing glitches, expired coupons, or code-dated products.
- Donating surplus food inventory to food rescue or food banks reduces warehouse storage and disposal costs.
How does the law protect businesses from liability?
The “Bill Emerson Good Samaritan Food Donation Act” ( Public Law 104-210) makes it easier for businesses to donate to food rescue and food bank programs. It protects donors from liability when donating to nonprofit organizations and protects donors from civil and criminal liability should the product donated in good faith cause harm to the needy recipient.
Tax benefits for donating food
Food donors are advised to consult with their tax adviser for information on tax deductions. For information on tax credit in California, please see the Chapter 503, Statutes of 2011 (Fuentes, AB 152), regarding donations to food banks, voluntary contributions, and income tax credits.
Potential Funding for Food Banks
Recycling Market Development Zone Loan Program. Food banks may qualify as a “recycling manufacturer” under the waste prevention category for CalRecycle’s Recycling Market Development Zone loan program. The loan can provide funding for working capital, daily operating expenses, equipment, such as trucks and refrigeration units, leasehold improvements, such as expanding an existing building, and real estate.
Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund Loan Program. Food banks may also be a part of an organics composting/anaerobic digestion project and the organics infrastructure project may qualify for CalRecycle’s Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund loan program, which can provide funding for equipment, real estate, and leasehold improvements.
There are additional funding programs that food banks may be able to utilize:
- IBank Financing Programs (California Infrastructure and Economic Development Bank or IBank)
- California Capital Access Program (California Pollution Control Financing Authority)
See the Small Business Success Story article in IBank’s newsletter for an article about Hope of the Valley Rescue Mission receiving funding via the State Loan Guarantee Program.
More information
- Information for Local Government
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Gleaning ToolkitPDF download
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Food Donation
Resources
For more information contact: Food Scrap Management, organics@calrecycle.ca.gov